Table of Contents

Related Pages
Staking crypto assets can seem like a daunting process, but it’s much easier than mining or trading. By using centralized exchanges or staking platforms, most investors find it much easier to jump into staking to generate wealth.
This beginner’s guide covers the basics of staking: methods, platforms, and the best crypto to stake for solid yields.
What’s Inside?
- Learn how to stake popular tokens like Ethereum, Cardano, and Solana right from your couch.
- Discover the best platforms and rates for some of our favorite staking tokens.
- A step-by-step guide to starting staking on Coinbase, Binance, and even your hardware wallet.
- Risks & Rewards: Yes, there’s fine print. We cover that, too.
How Do You Stake Crypto?
The simplest way to start staking as a beginner is via an online crypto exchange or platform. These resources provide users with tools and interfaces that make staking crypto straightforward.
Here’s an easy-to-follow guide to getting started with staking using Coinbase:
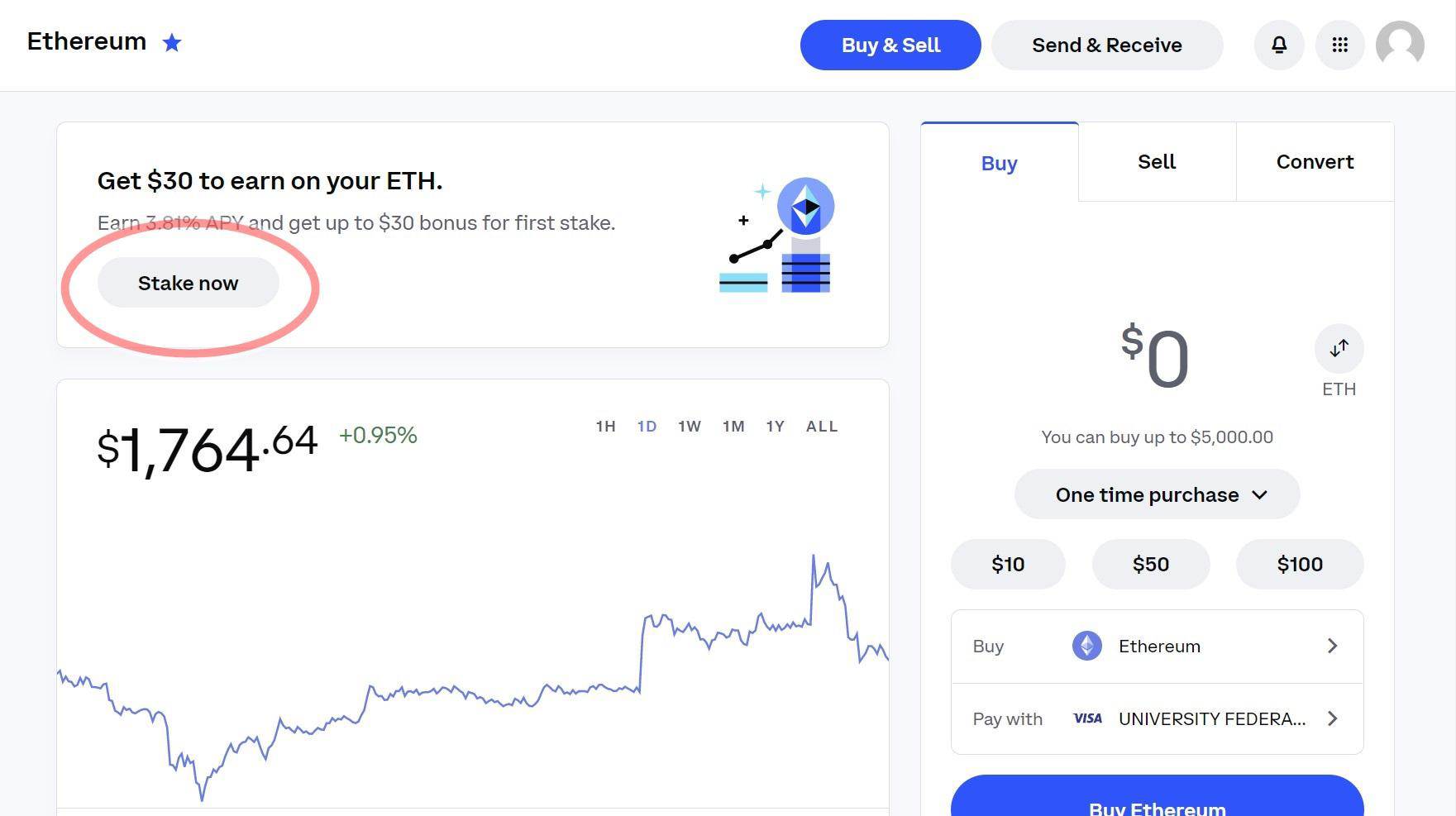
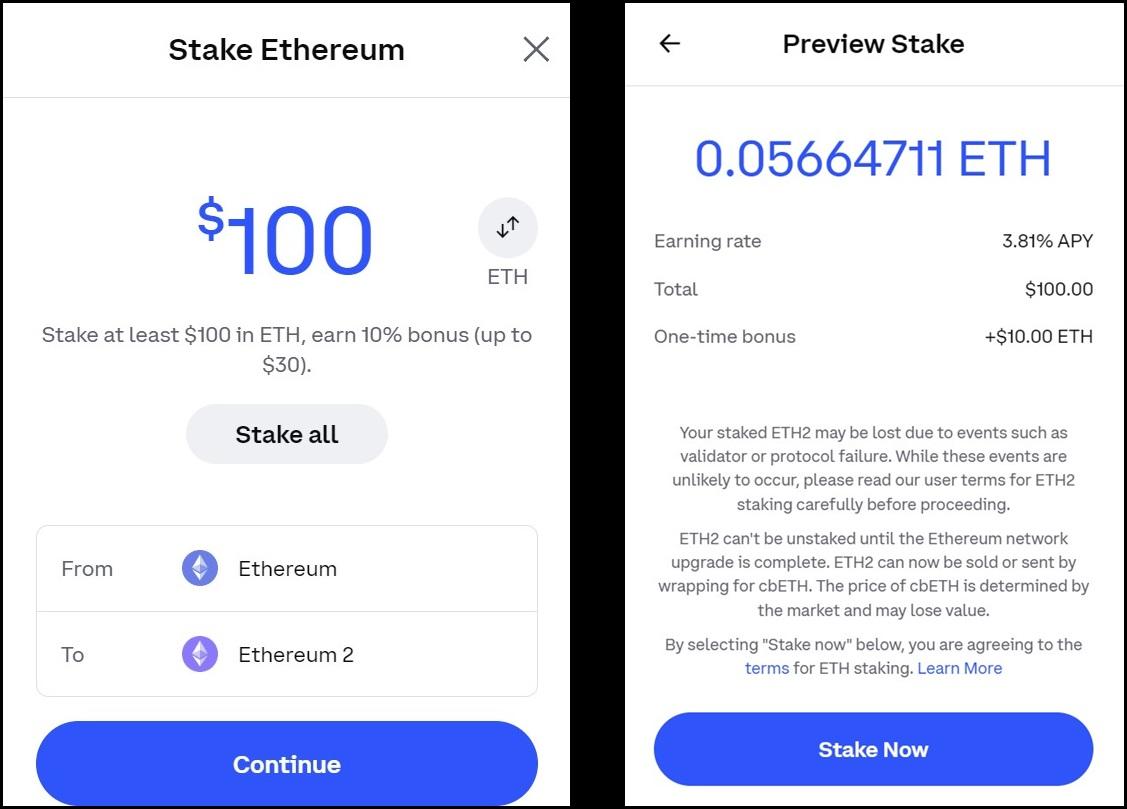
What is Staking Crypto?
Staking crypto is a process where investors can earn more cryptocurrency by supporting validation, specifically on “Proof of Stake” blockchains.
In a PoS blockchain, active users put up a small amount of crypto (the “stake”) to be considered for block verification. The chain will then select a random staker to authenticate a block and earn more crypto in return.
With the rising popularity of staking, however, it takes more and more crypto to participate effectively:
Staking is using your crypto to earn passive returns by locking some of that crypto into a staking wallet that the exchange uses to validate on-chain transactions. This process is much like earning “interest,” but rather than earning interest through a bond or a bank account, you earn it on the exchange.
Commonly, the staking process involves leaving the crypto in the wallet for a predetermined time. During this time, the network uses the locked cryptocurrency to verify transactions and maintain the security of the blockchain. In exchange for providing this service, crypto holders earn more cryptocurrency as a reward (i.e., “staking rewards”).
Staking is an alternative to the energy-consuming and tedious validation processes found on Proof of Work chains like bitcoin. You can earn interest income on cryptocurrency holdings without trading or mining it actively.
Proof of Stake vs. Proof of Work
Staking is possible exclusively on blockchains that employ the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus algorithm. This mechanism lets network participants agree on which transactions should be validated and added to newly created blocks.
Unlike bitcoin’s Proof of Work (PoW) algorithm, which raises the question “Can you stake bitcoin?” (the answer is no), the PoS consensus method is a more energy-efficient, eco-friendly alternative to PoW mining.
If you have PoS crypto investments sitting idle, staking is an option to earn additional income. It is similar to earning interest on a fixed deposit but with the potential for higher interest and risk.
How Crypto Staking Works
Staking involves holding a certain amount of cryptocurrency in a specific digital wallet and locking it in place for a predetermined amount of time. This process requires user resources to support stability and security across the chain, as staking wallets support the longevity of transaction verification.
To stake, users commit a certain amount of cryptocurrency to the network to participate in cryptocurrency staking. For example, a minimum of 32 ETH is required to stake on the Ethereum chain. The network then selects validators from among staking participants to confirm blocks of transactions. The more cryptocurrency users commit, the higher their chances of being chosen as a validator.
As each block is added to the blockchain, new coins are created and distributed as rewards to the validator of the block. Typically, these rewards are paid in the same cryptocurrency that the participants have staked.
Staking rewards vary depending on factors like the amount, the length of time the cryptocurrency is staked, and the demand for the cryptocurrency.
Different Ways of Staking
There are four primary ways in which you can participate in coin staking:
Delegation
The first and easiest way is delegating, a popular option for smaller crypto investors who don’t want to spend the money and effort to operate a validator. Rather than investing a large sum, smaller users delegate their coins to a validator (such as an exchange or staking platform), which pools the staking funds from multiple investors.
Investors then receive a portion of the staking rewards earned by the validator in exchange for their delegation. The rewards depend on the amount of the delegated cryptocurrency and the share it represents from the validator’s total stake.
Delegating implies entrusting your cryptocurrency to a third party. Therefore, it’s essential to perform due diligence and pick a trustworthy validator or node with a good track record and reputation in the network.
Pooled Staking
The second method is to stake your tokens through a pooled staking service. Many include Stake.fish (covered in more detail below) and RocketPool. Pooled staking functions similarly to a delegated approach in that a pool of crypto exists for staking purposes. However, this approach combines multiple validators into a pool to achieve greater staking rewards. The greater the number of tokens held in a single pool, the greater the chance that the pool will receive a staking reward. Pools are more advanced when compared to delegation but are worth investigating.
Liquid Staking
A third method for staking, becoming increasingly popular, is liquid staking services (also called liquid staking derivatives, or LSDs). Liquid staking through a platform like Lido (covered in more detail below) allows token holders to receive staking rewards while retaining access to their tokens. This provides greater flexibility and efficiency when staking. That said, liquid staking may be beyond those completely new to staking.
Validator Nodes
The fourth and most advanced method for staking is as a validator. You run your staking node using advanced technical skills and your hardware (which must always be kept online). The advantage is higher rewards and voting/controlling rights on some blockchains.
But becoming a validator takes work; you must invest higher sums just to qualify. And, of course, there’s the technical knowledge required. Running a validator node is certainly not for most beginners.
Popular Staking Tokens
Below are six of the more popular tokens we see staked by investors. Their popularity stems from several factors, including the project’s strength, the APY offered, and the token’s large market cap and liquidity.
The tokens discussed here are listed in order of the total percentage of tokens staked.
 Ethereum 2.0 (ETH2)
Ethereum 2.0 (ETH2)
After years of anticipation, Ethereum finally upgraded to PoS, with the Merge upgrade in September 2022. Many expect the shift to help the blockchain overtake bitcoin as the most valuable crypto by 2023-24. Still, whether Ethereum manages to dominate the crypto market remains to be seen. At this writing, ETH has a market cap of over $196 billion, about 39% of bitcoins.
Validator nodes on the new PoS blockchain require 32 ETH tokens and a lock-up of 365 days. Delegate staking pools don’t have any minimum requirements or lock-up periods, making them ideal for beginners. APYs for ETH staking will vary from one platform to another. We have many of the top staking platforms and ETH APYs here.
 Binance (BNB)
Binance (BNB)
Binance is the world’s largest cryptocurrency exchange. The platform launched a native token in 2017. With a $214 per coin value and a market cap of $32.9 billion, the Binance token is only behind bitcoin, Ethereum, and USDT on the list of largest cryptos.
To get started with BNB delegation pools, a minimum of 1 BNB is needed. However, you will need a whopping 10,000 BNB tokens to run a validator node. Both options have a minimum lock-up of 7 days, although longer periods result in higher reward rates.
 Polkadot (DOT)
Polkadot (DOT)
Polkadot uses a complex architecture of multiple chains to avoid the high fees and congestion plaguing other blockchains like Ethereum. Launched in 2020, the blockchain has zoomed to the top 15 cryptos list with a market cap of $5.1 billion.
Staking on this blockchain uses the native token DOT. The amount of DOT needed to stake is dynamic. based on factors like how much stake is being put behind each validator, the size of the active set, and how many validators are waiting in the pool. The current requirement is 450 DOT.
To join a delegated pool, you need a minimum of 1 token and a lock-up period of 28 days for what have historically been high APYs.
 Solana (SOL)
Solana (SOL)
This particular blockchain launched heavily on decentralized finance (DeFi). The SOL tokens were first publicly launched in 2020 for $0.22. In 2021, SOL was worth close to $250, placing it in the list of the top crypto with a market cap of $74 billion. SOL was hit by the “crypto winter,” but it remains one of the largest cryptocurrencies, with a $7.9 billion market cap.
No minimum limit is required to run a validator node on the Solana blockchain. Both delegator pools and validators have a lock-up of 2 days. The shared rewards from a pool can bring in around 7% APY.
 Cardano (ADA)
Cardano (ADA)
Cardano is another “Ethereum-killer” that has been around for nearly a decade. This PoS blockchain with smart contracts and improved scalability was launched in 2015. As of this writing, it is one of the top ten largest cryptos in market cap, with $8.9 billion.
Staking on ADA has several advantages – minimum limits or lock-in periods are not required. Users who join any large and reputable delegated pool can start earning rewards with minimum fuss. The APY for Cardano staking is around 5%.
 Tezos (XTZ)
Tezos (XTZ)
Launched in 2014, Tezos is a programmable cryptocurrency supporting smart contracts. It has a self-amending mechanism to avoid “hard forks” or compatibility divergence in two versions of the same blockchain. While the total market cap is a bit low at $684 million, many investors feel it has future potential.
To become a full validator or “baker” on the Tezos blockchain, you need a minimum of 6,000 XTZ and an initial lock-up period of 14 days. But if you don’t have enough tokens to spare, you can participate in the delegator pools for annual percentage yields (APY) of around 4%.
Where to Get Started with Coin Staking
There are three main places where you can stake PoS cryptos:
- Centralized Exchanges (CEX) – Most leading cryptocurrency exchanges, such as Binance and Coinbase, provide easy staking as an option to their users. This option is quite simple and allows you to take advantage of any useful features or regards the platform offers.
- Staking Platforms – These online “staking-as-a-service” platforms focus entirely on crypto staking pools in exchange for a commission. While less comprehensive than an exchange, these allow you to focus on staking.
- Hardware Wallets – This method using offline crypto wallets/hardware wallets is called cold staking.
Let’s take a closer look at some popular coin-staking options from these three categories:
Centralized Exchanges
 Binance (CEX)
Binance (CEX)
Binance is the largest and most popular crypto exchange worldwide. Apart from staking its native Binance Coin, you can pick from over 12 POS staking options, with APYs up to 13.5% or more. Staking information for Binance can be found here, along with a good explainer video.
 Coinbase (CEX)
Coinbase (CEX)
Established in 2012, Coinbase is a fully-regulated crypto exchange in the United States. The platform offers staking on all major PoS cryptos like ETH2 and Tezos. The NASDAQ-listed company is a top alternative to Binance, especially for US customers. Get started by opening a Coinbase account and visiting their Earn page for available assets to stake.
Hardware Wallets
 Ledger
Ledger
Ledger is the most popular brand for hardware crypto wallets. Using the Ledger Live app, you can connect to over 15 different Web3 services, many of which allow staking. The rewards are delivered on the Ledger Live app or to an external wallet. This makes most of the popular tokens available for staking through your Ledger wallet, including Ethereum, Polkadot, and Solana.
 Trezor
Trezor
Created in the Czech Republic in 2011, Trezor is the world’s first digital cryptocurrency hardware wallet. Trezor also supports crypto staking, but not directly. Instead, you can connect the Trezor to a wallet like Exodus as a staking interface. More advanced users can connect the Trezor to a staking service like Allnodes.
Staking Services
 Lido
Lido
Lido is a secure protocol for liquid staking that is designed to support multiple PoS cryptocurrencies, including Ethereum (ETH), Solana (SOL), Polygon (MATIC), Polkadot (DOT), and Kusama (KSM). Lido, launched in 2020, aims to solve the problem of the PoS staking ecosystem: illiquidity.
As a rule, once a crypto user starts staking, the assets are typically locked up and cannot be used or traded until the period ends. Lido aims to address this by allowing users to stake their cryptocurrency and receive a so-called “liquid staking token” (LDO) in return. Liquid staking tokens can eventually be traded or put to work in decentralized finance (DeFi) applications.
This makes it easier for users to participate in staking and access the benefits of staking rewards without sacrificing liquidity.
While Lido supports multiple PoS blockchains, the staking service focuses on Ethereum, the second-largest cryptocurrency by market cap, dominating the DeFi space.
 Stake.fish
Stake.fish
Stake.fish is a staking platform for cryptocurrencies where crypto holders can pool their assets and earn rewards. Stake.fish supports staking on 18 PoS blockchains, including Cardano, Cosmos, Ethereum, Polkadot, Polygon, Solana, and Tezos. At the time of writing, over 735,328 ETH is staked with the platform.
Launched in 2018, stake.fish has attracted over $1 billion worth of cryptocurrency for staking from both retail and institutional investors.
How to Stake Cryptocurrency: Step-by-Step Guide
The steps for staking will vary depending on the platform/method you prefer. However, the initial steps remain the same across all methods. Here are the simple general steps on how to stake cryptocurrency:
Basic Steps
- Choose a Crypto Asset to Stake: Look at factors like APY rewards, minimum stake, lock-up periods, and other aspects of the crypto asset. Do adequate research before picking up unknown/obscure cryptos.
- Decide on a Validator or Delegator: The validator requirements are quite steep for some crypto assets. They also require desktop PC hardware with 24/7 internet connectivity. Setting up the node also requires advanced skills. Most beginners will choose the delegation route. In this case, choosing a delegator with a good history and reputation is best.
For Crypto Exchanges
- Create an account: Visit the crypto exchange and sign up for an account. Link your crypto wallet to your account.
- Buy Stakeable Assets: If you don’t already have particular coins or tokens in your wallet, buy them from the exchange.
- Go to Staking Page: Find the dedicated staking page for the crypto on the online exchange. Coinbase is here, and Binance here.
- Enter Staking Information: Using the platform’s interface, set your staking amount and settings. Some exchanges offer different pools with varying lock-ups, APYs, and other special features.
For Private Staking (Crypto Wallets)
- Download App: Software wallets support staking directly on the app. Some examples are Exodus and Trust Wallet.
- Pick an Asset that Supports Staking: Most PoS blockchains, such as Ethereum, Cardano, or Solana, will support staking. Make sure to hold your crypto assets on the app.
- Set Stake: Launch staking by tapping “earn now” or “start earning.” You can calculate potential rewards directly on the app.
Delegating (Platforms)
- Select a staking platform, such as Lido or Stake.fish. Some platforms, such as Stake.fish, require registration, so register.
- Go to the staking page that lists all supported coins for staking. Choose a crypto asset that you want to stake.
- Connect a wallet where you have your cryptocurrency stored. Some staking platforms, such as Lido, support multiple wallets, including MetaMask, Ledger, Trust Wallet, and Exodus.
- Start the staking process after confirming the amount and checking the reward rate.

Mining vs. Staking
For individual investors, staking is a much better alternative to crypto mining. The energy issues associated with mining are one of the major reasons why Ethereum shifted to PoS. After the shift, the Ethereum blockchain saw its energy costs reduced by 99%.
The following table illustrates the main differences between mining and staking on cryptos:
Both methods also have some striking similarities, as listed below:
- Both allow the pooling of resources for low but steady rewards
- Rewards are provided in the native cryptocurrency
The STAKEaway: How to Stake Crypto and Make Money
Staking doesn’t involve steep upfront/running costs of mining: no GPUs or mining rigs are required. It does not spike your energy bills and is extremely eco-friendly. For beginners, the best way to try staking is via an online platform.
Like all crypto-related investments, staking has a fair degree of volatility and risk. Pick established crypto assets, and avoid less-known altcoins to minimize risk exposure.
To learn the basics, consider starting small with popular assets like Ethereum (ETH) or Cardano (ADA). Then, do thorough research and always exercise caution when investing/staking crypto assets.
To learn more about earning money on crypto investments, including the best staking rates, subscribe to our Bitcoin Market Journal newsletter.
Crypto Staking Frequently Asked Questions
What is staking in cryptocurrency?
Staking refers to participating in a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism by holding a specific amount of cryptocurrency in a wallet to support the network’s operations.
How does staking work?
Once you stake your coins, they are ‘locked’ for a certain period and used to validate transactions and create new blocks. In return, you earn staking rewards.
What are the benefits of staking?
- Passive Income: You can earn additional coins as staking rewards.
- Low Entry Barrier: Generally, you don’t need specialized hardware as you would for mining.
- Energy Efficiency: It is more eco-friendly compared to PoW systems.
- Network Security: By staking coins, you contribute to the network’s robustness.
What are the risks involved?
- Locked Funds: Your staked coins are not liquid, meaning you can’t sell or transfer them until the staking period is over(though LSDs attempt to address this downside).
- Slashing: In some PoS networks, misbehaving nodes may lose some of their staked coins.
- Market Volatility: The value of your staked coins can fluctuate, affecting your returns.
How to stake cryptocurrency?
- Do Research: Learn about the specific cryptocurrency you are interested in staking.
- Choose a Wallet: Opt for a staking-compatible wallet.
- Transfer Funds: Move your coins to your staking wallet.
- Follow Staking Instructions: Each cryptocurrency and platform will have its unique staking process, often outlined in their official website.
Can I unstake my coins?
Yes, but it may require waiting before you can access your staked coins. The time and conditions may vary based on the cryptocurrency.
Is staking better than trading?
Staking and trading are different strategies with their own risk-to-reward profiles. Staking is generally more passive and less risky than active trading but may offer lower potential returns.
What’s the minimum amount required for staking?
This varies from one cryptocurrency to another. Some might allow you to stake with as little as one coin, while others may require a more substantial minimum investment.
How does staking compare to bonds?
Staking and bonds offer passive income but differ in risk and regulatory oversight. Bonds are generally lower-risk and well-regulated, while staking offers potentially higher returns but with more volatility and less regulation.
Can you stake Bitcoin?
No, you cannot stake Bitcoin as it uses a Proof-of-Work consensus mechanism, not Proof-of-Stake. However, some financial services offer to “stake” your Bitcoin for you, but this is more akin to lending rather than true blockchain staking.


