Table of Contents
Semantic SEO is a relatively new method of doing SEO that involves using semantic connections between your words to improve organic rankings. The catch here is that search engines like Google are moving in this direction and future-proofing your business is a priority to have an edge over competitors.
This guide will provide you with the necessary knowledge you need to launch, or improve, your online business. You will also have enough information to analyze the possible implications of Semantic SEO. Finally, you will learn how a process like this works and why it’s extremely beneficial, including Keyword Research and Onpage strategies with a twist.
This guide has been designed to cover a complex topic in layman’s terms. However, this is not a subject you should ignore. Semantic SEO has been a robust and long-term strategy ever since Google introduced BERT. The topics and relationships you will find during the research process will be a large part of your content strategy going forward!
What is Semantic SEO?
Semantic SEO involves creating content around topics or entities by leveraging semantic principles and structured data. It means satisfying every possible variation of users’ queries and query intent.
Modern search engines algorithms rely on semantics to understand the text, which is one reason why Semantic SEO can help you get better rankings.
The focus is not on keywords; it’s more oriented towards the intent and the needs of the user. Semantic SEO focuses on entities and their relationships to make your copy more descriptive and factually accurate. Entities have attributes, i.e. characteristics that define them and distinguish them from others.
Using factual language is key when it comes to Semantic SEO.
What is Semantic Search?
Semantic Search is based on Deep Learning models to serve relevant and contextual search results by understanding the intent behind users’ queries.
It’s an action performed by modern search engines like Google to implement NLP techniques to enhance search results. Semantic SEO is the practice of optimizing for Semantic Search; they are closely interrelated.
A system of this type favors websites that are more topical and has more connections. What we are going to do is use this fact to increase our chances of being perceived as authorities.
Relationship with Semantic Search
Specifically, Semantic Search is the way search engines do their jobs. Search Engine Optimization is the way people do their jobs. Therefore, it’s wrong to say that you can perform or learn Semantic Search. It’s just useful to know how it works to increase the effectiveness of your communication and understanding of what is happening.
In the last few years, Google has put more effort into improving its understanding of what people want and the actual words in the content. For this reason, it’s better to focus on the customer journey and on what people really want.
Your business should be able to serve their needs with the proper pages and a correct navigation structure.
SEO myths about the topic
Semantic SEO is a term that is affected by severe misinformation. The extremely technical nature of the topic makes it easy to get confused.
One important point is that Semantic SEO is not the same as using LSI keywords, and SEO services or tools that offer LSI keywords are incorrect. As explained by Google and shown by the Google patent expert, Bill Slawski, LSI would be quite outdated anyway.
The similarity with the content silo approach is evident but there are key differences. Content silos don’t take linguistics into account and stop at the level of internal linking. Semantic SEO requires more planning and work on the pages.
This strategy doesn’t replace Offpage SEO since backlinks are still an important ranking factor. It’s possible to rank for less competitive keywords in some markets without any backlink.
The best tip is to create great content first and promote it via PR outreach to ensure it gets to the right people. Semantic SEO doesn’t substitute or overwrite the effectiveness of strong ranking signals such as links.
How to start and requirements
Semantic SEO is generally beneficial for large projects or affirmed brands that have access to the right financial resources. Content creation can become quickly expensive for large topics and according to the level of expertise required.
This type of strategy requires a substantial initial investment that will pay off in the long run. There is no clear benchmark because different markets can have different standards.
How does it work?
Semantic SEO is based on Natural Language Processing (NLP), a branch of Machine Learning involved in the processing of human language for machines. Google uses NLP algorithms to index and understands what your text is about and especially the intent behind users’ searches.
It’s not possible to game these algorithms as in the past but you can improve the quality of your text to help search engines to rank your content faster.
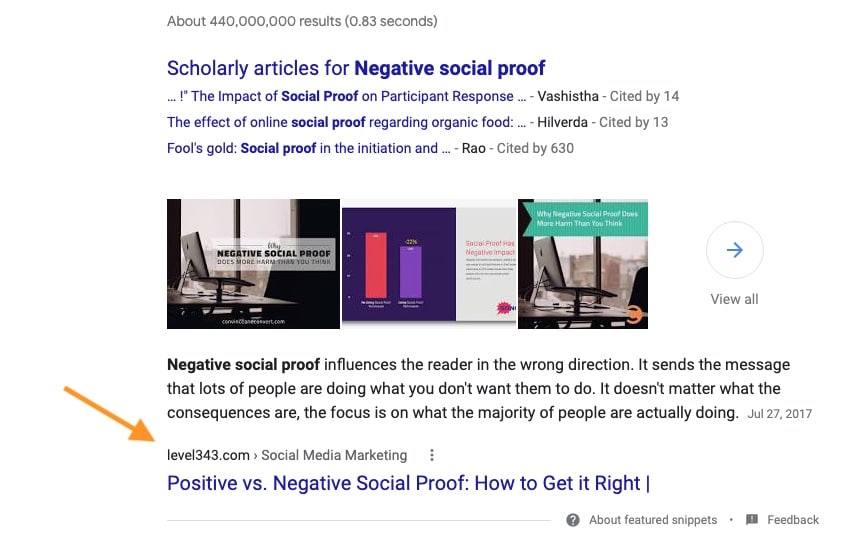
Google can parse your text and identify named entities, i.e. objects or concepts with attributes stored in a special database, called the Knowledge Graph. The inclusion of the right entities in your text can ultimately boost the so-called topicality of your website, making it more relevant to searches.
The traditional approach was keyword phrase matching, losing a lot of potential insights on the customer journey and possible related topics. Keywords depend on, and are heavily influenced by, the language since it’s what people are searching for.
Today, we look at entities. Entities are representations that Google can understand and do not depend on language.
A good structure with the correct entities and great content can make you an authority in the eyes of Google. This is essential to safeguard your website from future updates and prepare for MUM, a new model that will replace BERT and is said to be 1000 times stronger than its predecessor.
MUM will be able to combine results from different languages to provide unified search results. This could prove essential for large brands that can document a lot of their knowledge online.
Structured data is another part of the equation. In other words, you attach this metadata to your pages to explain to search engines what your page is about and its main characteristics. It’s a method to improve the understanding of your pages and increase the likelihood of being noticed.
Internal linking passes the value to different pages of your website and allows you to build semantic connections via anchor texts. If you are having trouble making a certain page indexed or even ranking, you can build meaningful ties within your content.
Creating topical maps
A topical map is just the overview of a topic. Let’s say your website is about cars. A topical map on cars will include manufacturers, models, types and other attributes that vehicles can have.
It’s an exercise to analyze something and get different content ideas that will be later mapped to keywords groups. Instead of using a bottom-up approach, we are doing the exact opposite here. This top-down methodology abstracts first and then goes into detail by finding related keywords that can complement our clusters of pages.
It seems quite simple but the process can be fearsome for complex topics. A good agency can help you in listing all the possible areas of growth for your business and this is a service that few can really offer.
Understanding your general direction is important because it allows you to shift into the right mindset. Knowing what to track and how to measure is necessary for digital marketing.
Where to find entities
Entities are everywhere and play the biggest part in the process. Our advice to find lists of entities is to look in the following places:
- Wikipedia pages, especially in English. These pages are often used to populate the Knowledge Graph so you can be sure they are important.
- Competitors ranking in top positions. There is a reason why they have the throne, try to understand what they say and how.
- Google Images suggestions, the grey boxes
- Google Knowledge Graph, you can query it via an interface or via the API (you need coding for this)
- Google Trends and Related Search Trends
- Google Autocomplete Data
- Common sense. If an entity is missing but makes sense for the topic, pretend it exists.
The idea is to cover as many topics as possible while preserving the logic for the user. Recall that this is an exercise to spot what to include and to find sweet spots that you can exploit. Deep expertise in the topics can make this process shorter.
Keyword Research
Entity research should aid what’s done during the creation of the topical map and complete it. You can use different tools inlinks.net and even People Also Ask (PAA) for maximum efficiency. The problem with this comprehensive approach is that you may lose focus and increase the scope too much. Another problem with a scope that is too wide is if you include topics not in the query corpus this will reduce page relevance for the query.
Since there is no fixed limit to how much you can go into detail, our advice is to use common sense and adjust the depth of your investigation according to the topic. The goal of keyword, entity and topic research is to determine the information to include in the page to completely cover the topic.
The practice in the past of creating new pages for keyword modifiers and query types (informational, transactional and navigational) is detrimental to completeness of the topic. Passage ranking will rank subtopics that would have been covered in additional pages.
There is no surefire way to know what to include. You can use common sense and analysis of information on the SERPs. If you notice that information is always referenced in related searches, people also asked and auto complete, it means you have to include it in your content.
Keyword and Entity Research should integrate your topical map and provide more context to what you have already done. Some may opt to skip it or reduce it depending on the niche. Most SEO tools lack data on some niches and that’s where Semantic SEO shines.
Onpage SEO and considerations
What you write on the page affects a Search Engines understanding and the HTML elements play a role in how search engines understand the context of the text. Google is able to detect unnatural sentences thanks to their syntax, if a part of a speech doesn’t make sense, your phrase won’t be understood as easily.
This is why you should always write for users and not search engines. They are trying to replicate how we behave to serve better results. It’s not always the case as shown by some SERPs populated by low-quality generated content, which will probably be removed after more Google updates.
Breadcrumbs, navigation menu and the footer contain key information for Search Engines because they tell more about the structure and the content of the website. This helps the users too and a good navigation menu helps to reduce the number of clicks needed to reach a certain page.
Other elements such as alt tags are not useful for ranking search results but are used for ranking in Google Images and are necessary to ensure accessibility by the disabled. Alt tags can tell a lot about the topicality of your images and you should always spend some minutes completing them.
Information gaps and unique value
The fastest win in content marketing is finding holes in your competitors’ strategies. Being able to provide unique information and playing on competitors’ mistakes is a strategy per se and it can be used to improve your value.
Search engines will consider you authoritative because you provide valuable and complete information not found anywhere, and is better when verified. Your value proposition will benefit because users can consume your content and perceive its distinctive worth.
A good Semantic SEO strategy should enhance your brand and bewitch your customers, like a strong content marketing strategy can accomplish. Finding those gaps and making them clearer is a good way to start differentiating yourself from competitors.
Topical authority and Topical relevance
There are no mainstream definitions to clearly outline these two terms.
Topical relevance refers to a website being relevant to a given topic/user search. If your website is strongly focused on food for dogs, Google will think it’s relevant to that topic. This doesn’t mean you will be the most relevant website out there by default, as there are several factors to evaluate this metric.
Once you have “passed” a certain threshold, your website can have topical authority. It’s very hard to rank for certain keywords without enough pages on that topic. If your business wants to expand into other markets and/or niches, it will be necessary to have some sort of proof that you are a reputable source of information.
Not even a solid backlink profile can help you without some topical relevance. There is one important caveat regarding topical authority: it can only be acquired after some time.
There are scenarios where you can see results after a few months (3 to 4), although the surprises come after more and more time.
Benefits of such an approach
Semantic SEO boosts the performance of content marketing campaigns for search engines by building connections within the content you have on your website. This implies that your content plan will be much larger and more methodical compared to that of most of your competitors.
This higher accuracy is beneficial for researching pain points and understanding better the customer journey and business requirements.
The main benefits of Semantic SEO are as follows:
- Holistic view
- Thought Leadership
- Better internal linking
- More stable traffic
Holistic view of your business and audience
The creation of a topical map itself is a process aimed at understanding in detail how to cover extensively a certain set of topics to satisfy your customers or attract new ones. This will make it easier to define an SEO roadmap with measurable objectives for your content and will save you a lot of time and effort in the future.
The best time to plant a tree is as soon as possible because it takes time to grow one. Your competitors may try to do the same and such a strategy is slow. While other businesses try to recover their lost advantage you can continue to build your own and improve your content.
Thought Leadership
Having content that ranks and is visible on search engines contributes to the creation of thought leadership, a very desirable achievement nowadays. A thought leader can set new trends and is an authority in that specific industry. A business with a leadership position gets a higher share of the market and is more likely to be TOMA, in other words, you can get more qualified leads.
An extensive network of great content showcases your deep knowledge of some problems and makes you more credible in front of your potential customers. Building a solid reputation in a competitive landscape should be a top priority for large businesses to defend their brand.
And the best way to persuade people into buying something is to make them spend time with you and content is the right companion for this task. A plethora of content can be mapped to define a clear customer journey and increase the likelihood that your customers buy from you.
Better internal linking structure
This improves the internal structure of your website, which is perceived as more authoritative by Google and can be rewarded with higher rankings. Search engines want to serve the most complete answers and to feature authoritative websites capable of answering every possible question about a topic. You cannot optimize your website for the past but you can future-proof yourself and improve your value proposition by following this approach.
More stable traffic
Seasonality can be great but what about achieving consistency? It’s easier to forecast something that tends to have little variation.
No one can guarantee what Google will do for sure, yet we can minimize the risk of relying on inconsistent topics. Evergreen content is a solid way to get consistent leads and shield you against fluctuations.
Possible downsides and complications
This approach is not without problems. One of the possible downsides is that it could take at least one year to grasp and benefit the full effects of Semantic SEO. For instance, Google can fully understand your content after some time, according to several factors, like the authority of the website.
You can see results in less than 6 months in some cases but, the best outcomes usually take more time. This makes Semantic SEO ideal for every business that wants to play long term and is ready to invest the resources and the time to produce a long-lasting momentum.
Since this strategy is about tagging content with the proper structured data and content, your website should already be in good shape. It is suboptimal to move to the content without having cleared all the serious issues that can affect your discoverability from search engines.
For this reason, we recommend Semantic SEO to large businesses that are just starting with their content or that want to bring their content to the next level and discover untapped opportunities.
Why should a business invest in Semantic SEO?
Google is already using advanced Machine Learning models to rank websites and this should be enough to convince you. Semantic SEO takes advantage of the semantic nature of a website to create a long-lasting competitive advantage.
Most of the reputable websites in some niches have strong semantic connections and they can boast a solid backlink profile. The main problem with delaying building your organic presence is that Google is getting pickier and focused on the customer journey.
A full-fledged Semantic SEO strategy can help start documenting and defining what your business needs are. Always think of SEO as related to your value proposition and to your knowledge.
While many people can be skeptical about this, it only makes sense that a billionaire company like Google would invest in honing advanced systems. Better systems mean improved results which translate to more money for them.
For all these reasons, it’s quite convenient to get started in this type of SEO.
Examples in some industries
There are many examples of successful applications of this strategy and some are not even aware of that. Wikipedia is such an example, it has a semantic network in place where everything is connected. Their internal linking strategy is excellent and allows the users to look for more and more information.
At the same time, this provides semantic clues to the search engines since they have really good anchor texts. Pack all of this with good images and unique content and you get an SEO powerhouse.
The same concept can be applied to other types of encyclopedic content on the web. Websites with factual and complete information have the edge over others.
A business doesn’t have the same time and resources to replicate the same success in a short amount of time. You don’t need to write extensive content on a topic if it is not necessary.
The best method is to start gradually and work on content on different steps of the topical map. You can take some branches and work on them for 6 months and then continue later on.
Content ideas are infinite and you should always continue to work on improving your website’s relevance to a topic.
The structure of a website should be consistent through time and be changed as little as possible. Spend more time on defining a good one that will last instead of sketching one and using it right away. Redesigns can cost important traffic and slow down your work.
For this reason, it’s highly recommended that you brainstorm all the possible topics for your website first.
How important is the structure of a website for Semantic SEO?
According to the niche and model of the website, the structure can play a key role in ranking higher. You should always have a navigable structure that makes sense for the user. In some cases, structure and URL paths are less relevant to your strategy.
Ecommerce is an example of the opposite. A good structure, breadcrumbs, and an efficient internal linking strategy are all necessary to prepare the field for more advanced changes.
In case of a large publisher, you don’t always need to have the same level of detail. In this scenario, content is way more important and the difference is played based on the content velocity and relevance of your website.
Since there are no disadvantages to having a good structure, prioritize it as soon as possible and be sure to create flexible schemes. If you need to add a subcategory in the future, be sure to have the space!
Implications for the future of search engines
Google is already investing and using NLP technologies to serve results to the users. While it’s not possible to directly trick or optimize these algorithms, implementing a solid content strategy that follows innovative principles, will.
Addressing certain issues now is the best way to avoid spending more resources later on and to minimize the risk of getting penalized by algorithm updates. Larger websites can be severely affected by Google updates and lose a lot of traffic, resulting in millions of dollars of potential losses, if not more.
Semantic SEO is a way to reduce this risk while allowing you to concentrate on building meaningful connections among pages of your website. Consistent research for a better value proposition is a benefit both online and offline.
The future competitive landscape will be harder and most likely based on extreme content quality and completeness. Non-English speaking countries offer better opportunities in terms of investment due to minor competition, although this can change.
Invest in your business by booking a consultation with a content marketing expert at Level343 and put your lead generation in the hands of a professional today.

